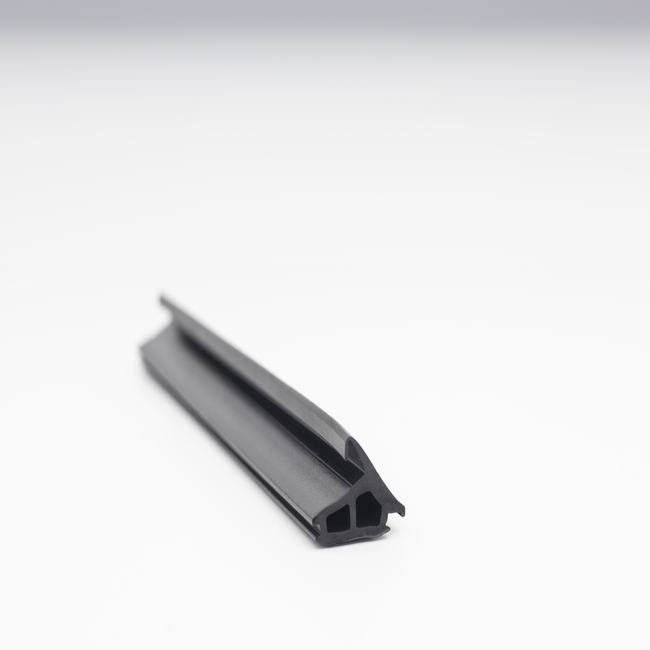
Industrial seals are vital components used in various industrial applications to prevent the leakage of fluids or the ingress of contaminants in machinery and equipment. These seals are designed to provide a secure and reliable barrier in challenging industrial environments. Below is an extensive description of industrial seals:
1. Function:
Industrial seals are designed to serve multiple functions in various industrial settings:
- Leakage Prevention: The primary purpose of industrial seals is to prevent the escape of fluids, such as liquids, gases, or powders, from machinery or containers. This is essential for maintaining process integrity and avoiding environmental contamination.
- Contaminant Exclusion: Industrial seals protect machinery and equipment from the ingress of contaminants, including dust, dirt, moisture, and foreign particles, which can lead to equipment damage and operational inefficiencies.
- Vibration Damping: In some applications, seals help dampen vibrations and reduce wear and tear on moving parts.
- Temperature and Pressure Resistance: Industrial seals must withstand extreme temperature and pressure conditions, ensuring they maintain their integrity and performance in challenging industrial environments.
2. Types:
Industrial seals come in various types to meet the specific needs of different applications:
- Gaskets: Gaskets are flat seals placed between two surfaces to prevent fluid or gas leakage. They are commonly made from materials like rubber, silicone, cork, or metal.
- O-Rings: O-rings are circular seals typically made of rubber or elastomeric materials. They are used in a wide range of applications to create a tight, circular seal, preventing fluid or gas leaks.
- Lip Seals: Lip seals, also known as oil seals, are used to prevent the leakage of lubricating oil or other fluids in rotating shafts. They have a flexible lip that makes contact with the rotating surface.
- Mechanical Seals: Mechanical seals are used in rotating equipment like pumps and compressors to prevent leakage at the point where the shaft enters the housing. They are commonly used in applications involving high pressure or corrosive fluids.
- Expansion Joints: Expansion joints are flexible connectors used in piping systems to absorb movement caused by thermal expansion, contraction, or vibration, while maintaining a tight seal.
3. Materials:
Industrial seals are made from a wide range of materials, each selected based on the specific requirements of the application. Common seal materials include:
- Rubber and Elastomers: Such as nitrile, EPDM, silicone, and Viton, offer flexibility and resilience, making them suitable for many applications.
- Metal: Stainless steel, carbon steel, and other metals are used in seals for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): Known for its excellent chemical resistance and low friction, PTFE is used in seals for corrosive environments.
- Graphite: Graphite seals are often used in high-temperature applications, including those involving extreme heat and aggressive chemicals.
4. Design and Construction:
The design and construction of industrial seals depend on the type of seal and the application. Gaskets may be flat, while O-rings are typically circular in shape. Mechanical seals often consist of multiple components, including stationary and rotating elements, and are designed to withstand substantial pressure.
5. Installation:
Proper installation of industrial seals is critical to their effectiveness. It involves selecting the right type of seal, ensuring the correct fit, and often using specific installation tools or techniques. A secure, even compression of the seal is crucial to prevent leaks.
6. Benefits:
Industrial seals offer numerous benefits in industrial applications:
- Enhanced Equipment Reliability: By preventing fluid leaks and contaminant ingress, industrial seals extend the lifespan and reliability of machinery and equipment.
- Safety: Seals help maintain safe operating conditions by preventing leaks of hazardous substances.
- Efficiency: Industrial seals contribute to operational efficiency by minimizing energy losses and fluid wastage.
- Environmental Protection: They help prevent environmental contamination by containing potentially harmful substances.
7. Maintenance:
Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of industrial seals. This may involve checking for wear, damage, or signs of leakage and replacing seals as needed.
8. Applications:
Industrial seals are used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Oil and gas production and refining
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceuticals
- Automotive manufacturing
- Aerospace
- Power generation
- Marine and shipbuilding
- Pulp and paper mills
- HVAC systems
- Mining and construction equipment
In conclusion, industrial seals play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of machinery and equipment across a multitude of industries. They are designed to prevent leaks, contamination, and damage in challenging industrial environments, contributing to safety, reliability, and environmental protection. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance are key to their long-term effectiveness in various industrial applications.